nanocellulose impact testing|environmental impact of nanocellulose : retailer laser-induced projectile impact tests (LIPIT),52,53 MD simula- tions have successfully been used to explain the failure mech- anisms of nanomaterials subjected to ballistic impacts. WEBThe new Mult Porn is the paradise of porn comics and hentai comics, we have thousands of comics of the best genres like porn doujins, for lovers of furry porn comics we have excellent zoo comics, simpsosn porn, ben 10 hentai, pokemon porn or pokeporn as many know him, incognitymous, or television anime like my hero academia hentai, naruto .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webFútbol Libre TV - Partidos y canales online en vivo. Ver Fútbol libre TV online en vivo y en directo. Canales gratis para ver partidos del fútbol Peruano, Argentino, Chileno, .
Discovering the broad applications of nanocellulose in addressing the various emerging issues is the innovation in research and development (R&D). An outline of recent progress in nanocellulose is presented in the corresponding subsections. In this review, recent advances in the preparation, modification, and emerging application of nanocellulose, especially cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), are described and . In recent years, nanomaterials have displayed potential in effective detection and removal of greenhouse gases, chemical contaminants, organic pollutants, and biological . This review gives a comprehensive account of nanocellulose–water interactions and their repercussions in all key areas of contemporary research: fundamental physical chemistry, chemical modification of nanocellulose, .
laser-induced projectile impact tests (LIPIT),52,53 MD simula- tions have successfully been used to explain the failure mech- anisms of nanomaterials subjected to ballistic impacts. Nanocellulose. Abstract. Nanocellulose is a nascent and promising material with many exceptional properties and a broad spectrum of potential applications. Because of the unique and functional materials that can .
Several forms of nanocellulose, notably cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrillated cellulose, exhibit attractive property matrices and are potentially useful for a large number of industrial applications.In this study, ballistic impact simulations of CNC films with Bouligand microstructures were carried out using a previously validated, CG model of CNCs to investigate the influence of both the structural (i.e., γ) and mechanical (i.e., .
nanocellulose technology
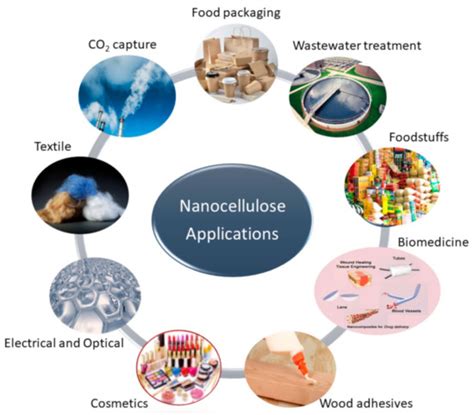
Although a number of comprehensive reviews on human health hazards of nanocellulose have been conducted, this paper brings new insights as it systematically analyzes and quantitatively assesses the results of in vivo . This review article provides an overview of nanocellulose as a sustainable material, covering the different properties, preparation methods, printability and strategies to . The results obtained in Table 4 show clearly that the addition of nanocellulose improves impact strength and Kc of epoxy composites. A double increase in impact strength was achieved with Ep0 + 1.5% NC. The other samples improved their impact strength by about 70–90% compared to the reference composite. Unmodified epoxy resin is a brittle .
Several forms of nanocellulose, notably cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrillated cellulose, exhibit attractive property matrices and are potentially useful for a large number of industrial applications. These include the paper .
Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) The surface morphology of pure PLA and CNC/PLA bionanocomposite filaments was nalysed by FESEM.1.2. Classification of biopolymer nanocellulose Biopolymer nanocellulose is classified into different forms based on the source and dimensions. The size range of biopolymer nanocellulose varies with different raw materials and the processing pre-treatments used. Mainly, nanocellulose can be classified into nanofibers and nanostructured . The test was performed using the conditions established in the ISO 846 standard . Degradation was measured at 7, 50, and 150 days. Results were illustrated as a function of weight loss percentage, which increased with time. . LCA results indicate that the environmental impact of nanocellulose is mainly dependent on the production path and the . Cellulose has a hierarchical structure ranging from micro to nano scale and much attention has been paid to nanocellulose because it is a renewable bio-based material with superb performance in .
Nanostructured cellulose (cellulose nanocrystals or nanocellulose) offers a high aspect ratio and mechanical strength that may support development of a new class of concrete adapted for extreme environmental conditions. . Destructive and nondestructive testing, along with surface morphology characterizations, were conducted to evaluate the .Cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) and nanofibers (CNF) have been broadly studied as renewable nanomaterials for various applications, including additives in cement and plastics composites. Herein, life cycle inventories for 18 previously examined processes are harmonized, and the impacts of CNC and CNF production are compared with a particular focus on GHG emissions. . Nomenclature and Types of Nanocellulose. Nanotechnology has become one of the driving forces behind a new industrial revolution in several fields, ranging from bionanocomposites, passing through medical, or even sensing and biosensing applications (Arof et al., 2019).Nanoscale materials have a size of about 100 nm in at least one dimension with .
Impact strength was recorded by using a Charpy type impact test. Surface roughness test was performed using a Contour GT machine. One‐way ANOVA and Tukey's post‐hoc analysis (p ≤ 0.05) were .Abstract The application of biomass-derived renewable materials has generated great interest in recent research works. Among many such biopolymers, nanocellulose has become the leading topic in the sphere of sustainable material owing to the outstanding mechanical, chemical and thermal properties along with non-toxicity, surface functionality, ease of modification and .Fig. 1 (a) Coarse-graining scheme showing the mapping between the all-atom model of CNCs (left) and the corresponding bead-spring representation (right); (b) a representative SEM image of the helicoidal microstructure of a mantis shrimp dactyl club (left, reprinted with permission Elsevier 14), with a schematic showing the ballistic impact simulations of a bioinspired CNC film with a .
Acute and chronic testing with fish and water fleas . University of Ottawa: Hatching and survival tests with Zebra fish . Environment Canada: Tests with various aquatic . Potential Impact of NanoCellulose • NanoCellulose has a substantial potential for . economic growth • Development of new products will lead to .
nanocellulose modification covers fresh ground by focusing on end-wise modification of CNCs and novel (mainly <2 year old) accounts on polymer grafting on nanocellulose, thus distin-guishing itself from the already well-known nanocellulose-based reviews,[11,17] or more specialized accounts without a broader materials perspective.[21–23] 2.
The biological impact of nanocellulose is portrayed in three other original research studies [13,14,15]. For instance, Bernier et al. investigated the impact of a library of cationic CNC in the human blood and endothelial cells using cell-based assays . They observe that despite the cationic CNC not changing RBC morphology or causing . Nanocellulose, a biopolymer, has received wide attention from researchers owing to its superior physicochemical properties, such as high mechanical strength, low density, biodegradability, and biocompatibility. . and the impact of the delivered drug on the metabolism pathway. The potential of nanocellulose-based composites has already been . Finally, the impact of the wood substrates on the shape fidelity/retention and mechanical properties of HCNC structures was then investigated via a three-point bending (TPB) test. . 3D-printed HCNC structures cross-sectional morphology after TPB test: a. 25 wt% concentration nanocellulose before post-curing; b. 25 wt% concentration .
Nanocellulose is the skeletal structure of wood and plant and has many advantages [5], . on the surface of the CNFs reduces the interfribril friction that facilitates the fibril-fibril slippage during tensile testing. Meanwhile, HEC is a cellulose derivative that does not dramatically decrease the tensile strength of the CNF-based film . Bacterial nanocellulose (BNC) membranes have enormous potential as systems for topical drug delivery due to their intrinsic biocompatibility and three-dimensional nanoporous structure, which can house all kinds of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Thus, the present study investigated the long-term storage stability of BNC membranes loaded with both .
nanocellulose size chart
Nanocellulose materials are used in producing low-calorie foods for handling weight disorders [234, 235], as well as used in producing highly porous materials with higher tensile strength such as nanocellulose papers, films, and aerogels for varied purposes [236, 237]. The capability of nanocellulose to produce porous aerogels and strong .
Cellulose is a natural and abundant polymer which can be derived from a large variety of materials such as biomass, plants and animals etc. Nanocellulose demonstrates remarkable physicochemical, mechanical, biological and structural properties. Technological challenges such as efficient extraction of cellulose and nanocellulose from precursors are still . The deviation from the average height has the highest impact on the . persistence length of individual nanocellulose chains. In order to test whether counterion condensation plays a role in the . Cellulose is the most venerable and essential natural polymer on the planet and is drawing greater attention in the form of nanocellulose, considered an innovative and influential material in the biomedical field. Because of its exceptional physicochemical characteristics, biodegradability, biocompatibility, and high mechanical strength, nanocellulose attracts .
Research on nanocellulose has significantly increased over the past few decades, owing to the various attractive characteristics of this material, such as renewability, widespread availability, low density, excellent mechanical properties, economic value, biocompatibility, and biodegradability. Nanocellulose categorized into two main types, namely cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) and . The impact force and shear force in fluid are generated to cleavage cellulose microfibrils into nanometer size in diameter. For examples, Li et al. [68] isolated nanocellulose from sugarcane bagasse by high pressure homogenization. The obtained nanocellulose had a diameter of 10–20 nm with lower crystallinity than the original cellulose.
One way Anova test results with p-value of 0.000 indicates differences in the six groups (p<0.05). Conclusion: This study concludes that the impact strength value of PMMA with the addition of rice husk nano cellulose has increased compared to the control group without the addition of rice husk nano cellulose. Nanocellulose (NC), due to its sustainable nature, high aspect ratio, superior mechanical strength, and availability of functionalizable OH groups, has been widely utilized as reinforcement in numerous fluids/plastics. The physico-chemical properties of NC, like surface characteristics, dimensions/aspect ratio and their concentration, significantly impact the .

edge compression test
nanocellulose research paper
Oggi é uma marca de móveis que oferece escrivaninhas e outros produtos para o seu ambiente de trabalho ou lazer. Conheça a história, as ofertas e as facilidades de .
nanocellulose impact testing|environmental impact of nanocellulose